Semi-Log and Log-Log Graphs
Let's take a closer look at the difference between semi-log and log-log graphs.
Plotting on Logarithmic Paper
Logs are helpful when plotting certain types of data. There are two types of log graphs that can be used when plotting data.
Semi-log Graph
The first is called a semi-log graph. In a semi-log graph the y-axis is logarithmic, which means the separation between the ticks on the graph is proportional to the logarithm of numbers. The x-axis has a linear scale, which means the ticks are evenly spaced.
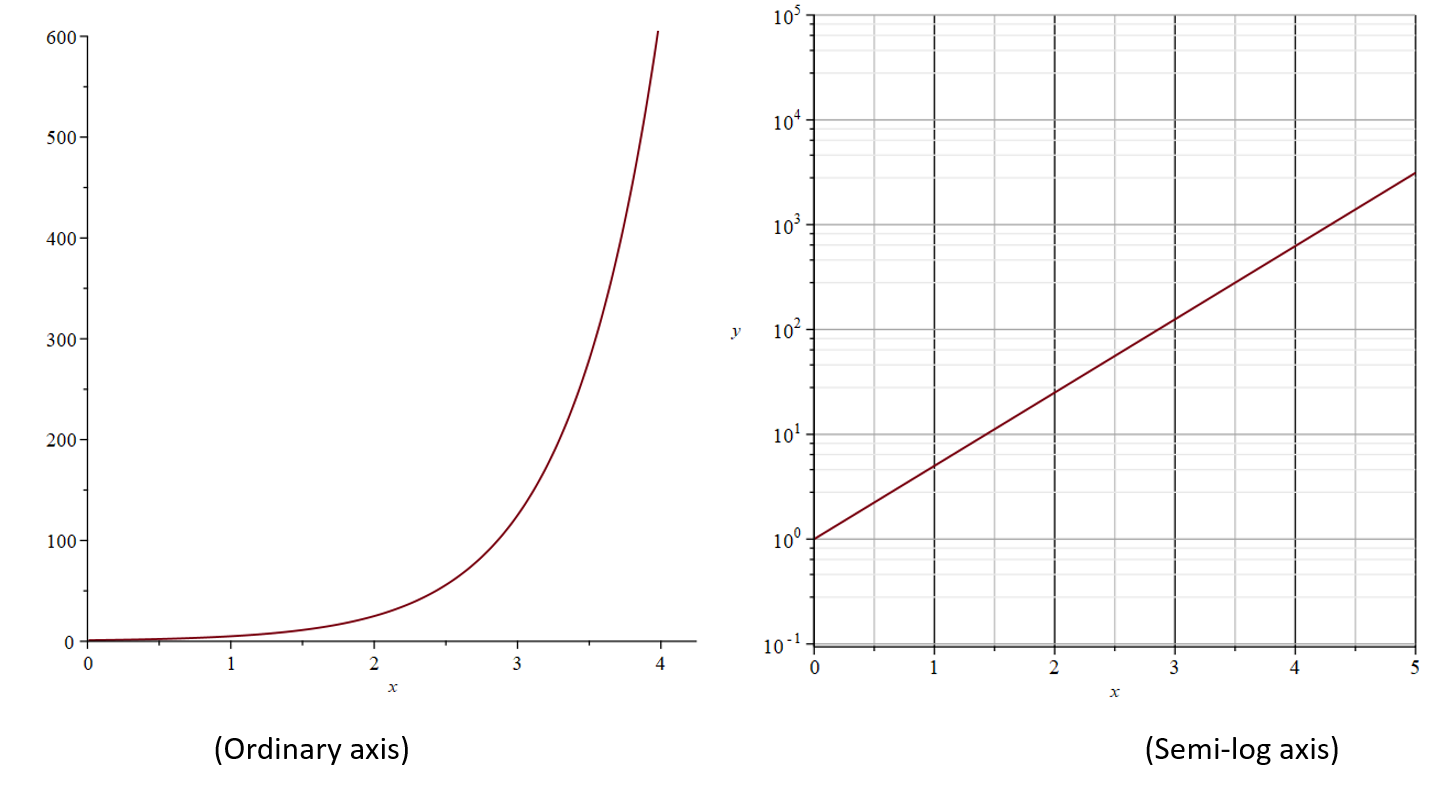
A semi-log graph is useful when graphing exponential functions. Consider a function of the form y = bax. When graphed on semi-log paper, this function will produce a straight line with slope log (a) and y-intercept log (b).
Example: Plot the function y = 5x on an ordinary axis (x- and y- linear scales) as well as on a semi-log axis.
Solution: Both graphs below:
Log-log Graph
The second type is called a log-log graph. In a log-log graph, both the x-axis and the y-axis are logarithmic.
This is useful for determining power relationships. If a function of the form y = axn is graphed on log-log paper, a straight line will be produced, with slope n and y-intercept log (a).
Semi-Log Graph Example:
Log-Log Graph Example:
