Pythagorean Theorem
Introduction
Suppose that we have a right-angled triangle (a triangle that contains a 90o angle) as shown below, where c is the side opposite the right angle (this side c is called the “hypotenuse”)
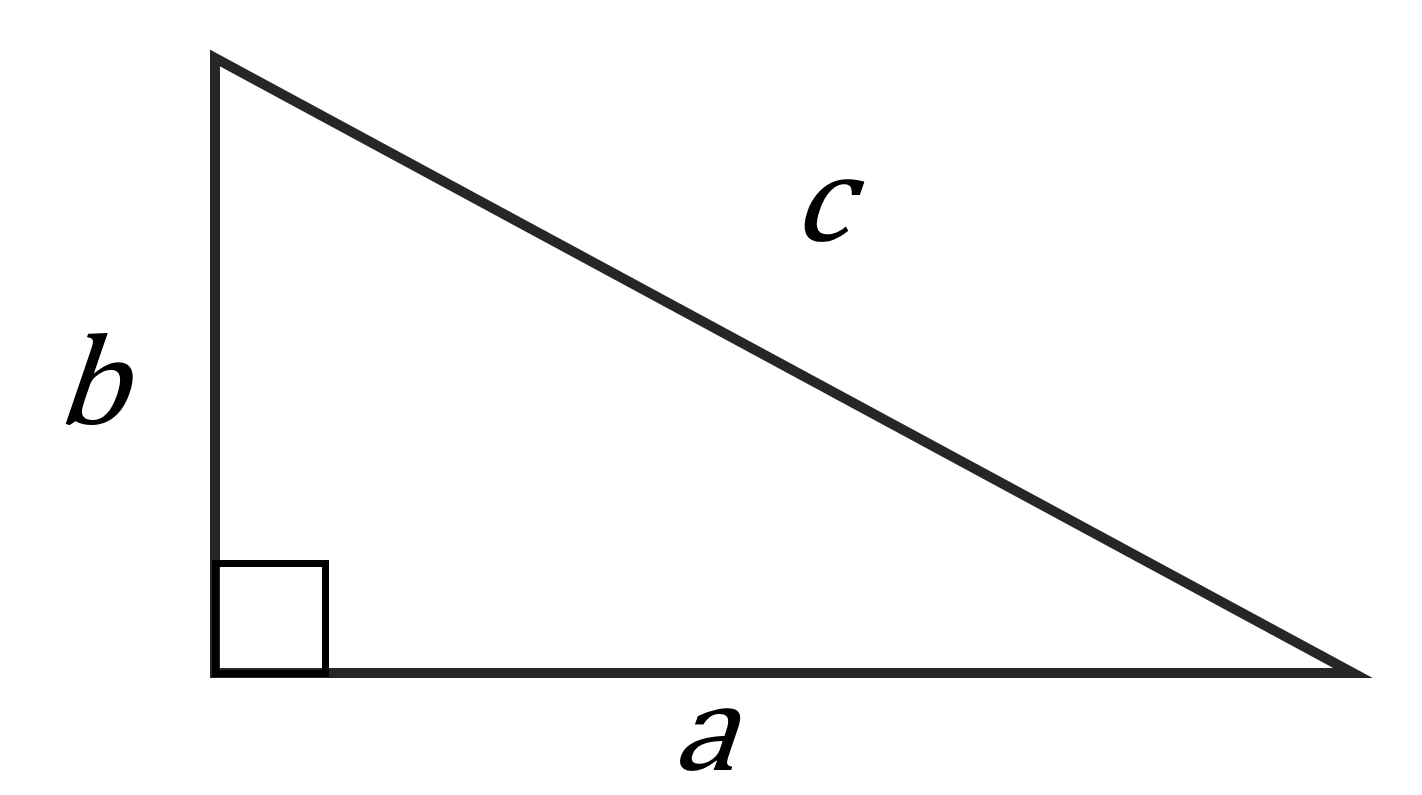
The Pythagorean Theorem tells us that the lengths of the sides are related by the following formula:
\[ a^2+b^2=c^2\]
Example:
If a right-angled triangle has one side of length 3 and one side of length 4, find the length of the hypotenuse.
Solution:
\( \begin {array}{c} a^2+b^2&=&c^2 \\ 3^2+4^2&=&c^2 \\ 9+16&=&c^2 \\c^2&=&25\\c&=&5 \end{array} \)
Therefore, the hypotenuse has a length of 5.
Example:
