Transformations of Trigonometric Functions
The transformation of functions includes the shifting, stretching, and reflecting of their graph. The same rules apply when transforming trigonometric functions.
Vertical and Horizontal Shifts
Suppose c > 0. To obtain the graph of
\(y = f(x) + c\): shift the graph of \(y = f(x)\) up by \(c\) units
\(y = f(x) - c\): shift the graph of \(y = f(x)\) down by \(c\) units
\(y = f(x - c)\): shift the graph of \(y = f(x)\) to the right by \(c\) units
\(y = f(x + c)\): shift the graph of \(y = f(x)\) to the left by \(c\) units
Example: Sketch the function \(y=\sin(x), y=\sin(x)+4,\) and \(y=\sin(x+\frac{\pi}{2})\).
Solution:
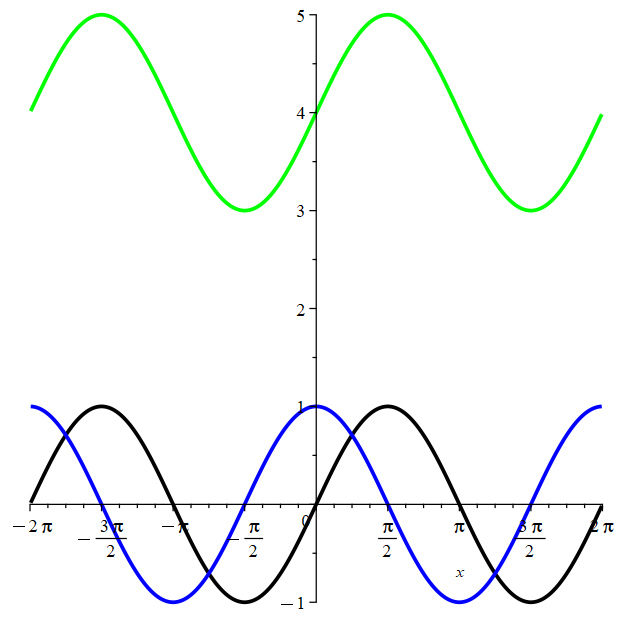
Here, \(y=\sin(x)\) is shown in black. The curve \(y=\sin(x)+4\) is shifted 4 units up, shown in green. The curve \(y=\sin(x+\frac{\pi}{2})\) is shifted \(\frac{\pi}{2}\) units to the left, and is shown in blue. Notice that this is the same thing as the curve \(y=\cos(x)\).
Vertical and Horizontal Stretches/Compressions
Suppose c > 1. To obtain the graph of
\(y = cf(x)\): stretch the graph of \(y = f(x)\) vertically by a factor of \(c\)
\(y = \frac{1}{c} f(x)\): compress the graph of \(y = f(x)\) vertically by a factor of \(c\)
\(y = f(cx)\): compress the graph of \(y = f(x)\) horizontally by a factor of \(c\)
\(y = f(\frac{x}{c})\): stretch the graph of \(y = f(x)\) horizontally by a factor of \(c\)
Example: Sketch the functions \(y=\cos(x), y=\cos(2x),\) and \(y=3\cos(2x)\).
Solution:
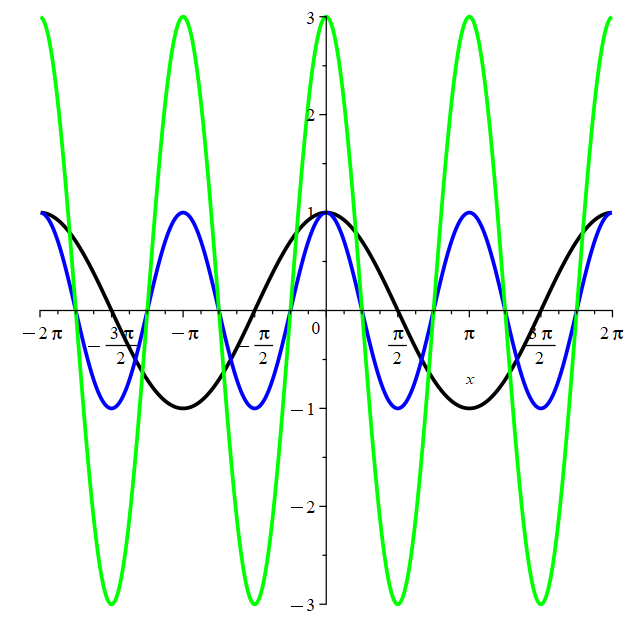
The function\(y=\cos(x)\) is shown in black. The blue curve represents the function \(y=\cos(2x)\) and is compressed horizontally by a factor of 2. The green curve represents the function \(y=3\cos(2x)\) and is the blue curve stretched vertically by a factor of 3.
Reflections
To obtain the graph of
\(y = -f(x)\): reflect the graph of \(y = f(x)\) about the x-axis; and
\(y = f(-x)\): reflect the graph of \(y = f(x)\) about the y-axis
Example: Given that the blue curve represents the function \(y=\sin(x)\), determine whether the following statement is TRUE or FALSE.
The green curve on the following graph represents both \(y=-\sin(x)\) and \(y=\sin(-x)\).
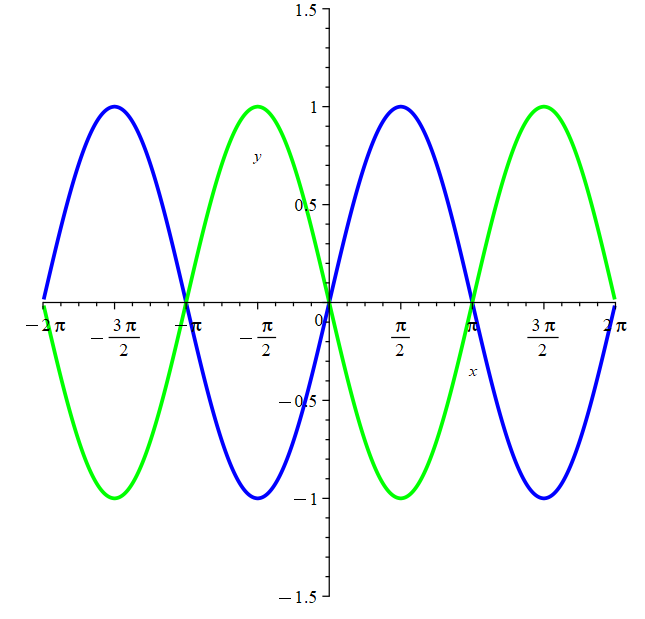
Solution: TRUE - The green curve does represent \(y=-\sin(x)\) and \(y=\sin(-x)\). In this particular situation the reflection about the x-axis is the same as the reflection about the y-axis.
Example 1:
Example 2:
