Stoichiometry
Once you are familiar with balancing equations, you will want to put this technique to practical use. You can do this with stoichiometry, which is using the ratios of reactant and product molecules for calculations. For example, if 2 molecules go in, how many can we expect to come out based on the balanced equation?
Let’s consider this equation:
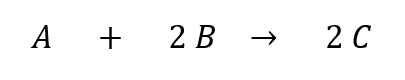
For every 1 molecule of A, we need 2 of B. These will react to make 2 molecules of C. But what if we’re not looking at exactly 1 molecule of A and 2 of B? Below is an example where we have 2 molecules of A and 4 molecules of B. This produces 4 molecules of C instead of just 2. The ratio of 1:2:2 from the original equation is maintained:
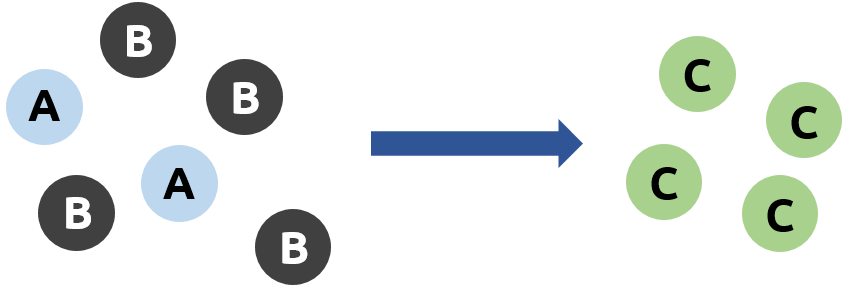
What if we don’t have a perfect ratio? Below we only have 1 molecule of A for every 4 molecules of B. Every time we want to make 2 molecules of C, we need 1 A and 2 B. Since we only have 1 A, it doesn’t matter how many molecules of B we have – we cannot make more than 2 C molecules:

This makes A the limiting reagent in this example, which means that the amount of product C we can make is restricted by how many molecules of A we have. This also makes B the excess reagent, because only 2 molecules of B react, leaving 2 molecules of B unreacted.
The mole
The coefficients in balanced equations represent the ratios of molecules to one another, but we need to be able to count molecules if we want to follow these ratios in the lab. However, molecules are exceptionally small, which means that typically we end up using huge quantities of particles – for example, a 1 gram sample of hydrogen gas contains nearly 3 × 1023 molecules! This isn’t really a practical number, so we need to have an easier way to count particles.
Think about how we count eggs – we usually count these in “dozens,” which is just a shorthand way to say “groups of 12.” But really, we can count anything in dozens, not just eggs! For example, 3 dozen people is just a group of 36 people. Likewise, 5 dozen molecules would only be 60 molecules. This is still not anywhere close to the number of molecules we would handle at once in the lab, so chemists have a similar shorthand for counting particles called the “mole” (units = mol) which represents a group of 6.022 × 1023 objects. This huge quantity is called Avogadro’s number (NA, units = mol-1).
We can convert any quantity of objects into moles using the following equation:
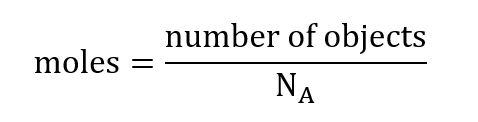
Example: In 2019 the population of Canada was measured to be 37.59 million (1 million = 106). How many moles of people lived in Canada in 2019?

This means that the population of Canada is only 0.00000000000000006242 mol! Calculations like this put into perspective just how many molecules are involved in chemical reactions, even on a small scale.
Converting between mass and moles
In the lab we usually measure chemicals by mass. However, we need to be measuring in moles if we want to use stoichiometry, because mass doesn’t reflect the ratio of atoms to each other. To put it another way, 10 grams of molecule A and 10 grams of molecule B generally won’t have the same number of moles of particles, because A and B each have their own molar mass (unit = g/mol) that determines how many grams make up one mole of the molecule.
Here’s how you can calculate moles from mass:
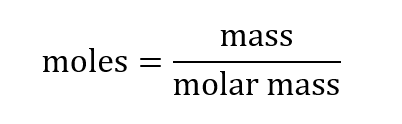
We can also rearrange this to calculate mass from moles:
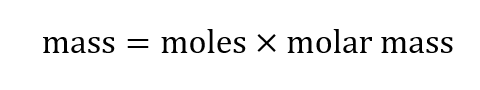
Let’s look at a couple examples:
Example 1: A chemist weighs a sample of magnesium sulfate (MgSO4), and measures a mass of 5.36 g. MgSO4 has a molar mass of 120.37 g/mol. How many moles of magnesium sulfate are in the sample?

Example 2: You need to prepare a 0.100 mol sample of NaCl for a reaction, but you can only measure it by mass. If NaCl has a molar mass of 58.44 g/mol, how many grams do you need?

